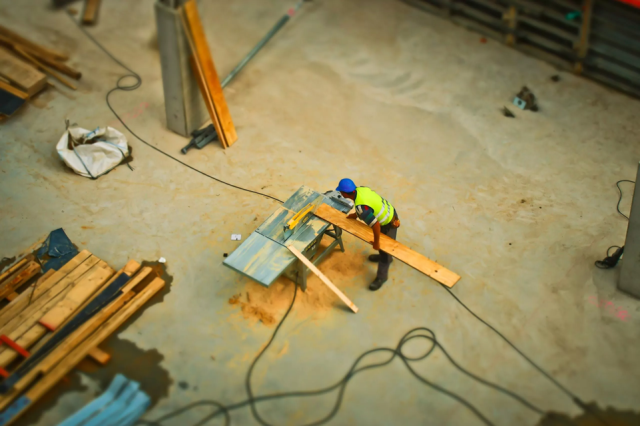
Hazards on a construction site can be categorized into several types, including mechanical, electrical, physical, ergonomic, chemical, biological, ecological, and others. Below is a list of these hazards:
-
Mechanical Hazards
- Machinery-related Injuries: Moving parts of machinery, such as cranes, excavators, and bulldozers, can cause crushing, cutting, or entanglement.
- Falling Objects: Tools, materials, or debris falling from heights can cause injuries to workers below.
- Vehicle-related Accidents: Collisions or run-overs involving construction vehicles or heavy equipment.
- Ladders and Scaffolding: Unsafe use or failure of ladders and scaffolding can lead to falls or structural collapse.
-
Electrical Hazards
- Live Wires: Contact with live electrical wires or faulty wiring can result in electric shocks or electrocution.
- Overhead Power Lines: Accidental contact with overhead power lines, particularly when using cranes or ladders.
- Portable Electrical Equipment: Damaged or improperly used portable electrical tools can cause shocks or short circuits.
- Temporary Electrical Installations: Poorly installed or maintained temporary electrical systems pose fire and shock risks.
-
Physical Hazards
- Noise: Prolonged exposure to loud machinery and tools can cause hearing loss or stress.
- Vibration: Vibration from tools like jackhammers can lead to hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS) or other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Radiation: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun or radiation from certain construction processes like welding.
- Extreme Temperatures: Exposure to heat (leading to heat stress) or cold (leading to hypothermia) in outdoor environments.
- Poor Lighting: Inadequate lighting can lead to accidents due to reduced visibility.
-
Ergonomic Hazards
- Manual Handling: Lifting, carrying, or moving heavy materials can cause back injuries, strains, and sprains.
- Repetitive Motion: Tasks that require repetitive movements can lead to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
- Awkward Postures: Working in awkward or confined spaces can strain muscles and joints, leading to injuries.
-
Chemical Hazards
- Dust and Fumes: Inhalation of dust from materials like concrete, wood, or asbestos, or fumes from paints, solvents, and welding.
- Exposure to Hazardous Substances: Contact with hazardous chemicals such as adhesives, sealants, or cleaning agents can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, or poisoning.
- Asbestos: Disturbance of asbestos-containing materials can release fibers that cause serious respiratory diseases.
- Silica Dust: Inhalation of crystalline silica dust, commonly found in construction materials, can lead to lung diseases such as silicosis.
-
Biological Hazards
- Mold and Fungi: Exposure to mold or fungi in damp or poorly ventilated areas can cause respiratory problems and allergic reactions.
- Rodents and Pests: Rodent bites or exposure to rodent droppings can lead to diseases like leptospirosis.
- Insects: Bites or stings from insects such as mosquitoes, bees, or spiders can cause allergic reactions or transmit diseases.
- Infectious Diseases: Close working conditions can facilitate the spread of infectious diseases, especially in poor sanitary conditions.
-
Ecological Hazards
- Soil and Water Contamination: Leakage or spillage of hazardous substances can contaminate the soil and water sources, affecting both the environment and human health.
- Disruption of Natural Habitats: Construction activities can lead to the destruction of local flora and fauna, impacting the ecosystem.
- Waste Disposal: Improper disposal of construction waste can harm the environment and create health hazards.
-
Other Hazards
- Fire and Explosion: The presence of flammable materials, such as fuels, gases, or solvents, can lead to fires or explosions.
- Confined Spaces: Working in confined spaces, such as tanks or underground tunnels, can result in suffocation, entrapment, or exposure to toxic gases.
- Slips, Trips, and Falls: Wet surfaces, uneven ground, or obstacles can lead to slips, trips, and falls, which are among the most common construction site injuries.
- Fatigue: Long working hours, physical exertion, and insufficient rest can lead to fatigue, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Violence and Harassment: Physical or verbal abuse, harassment, or bullying among workers can lead to a hostile and unsafe work environment.
-
Psychosocial Hazards
- Stress: High-pressure deadlines, job insecurity, or poor management can contribute to stress, affecting mental health and productivity.
- Isolation: Working in remote or isolated areas can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Nutshell
By identifying and addressing these hazards, construction companies can create a safer and healthier environment for their workers.