Key Points for Electrical Safety as per NFPA 70E
-
Objective of Electrical Safety Training
- Protect workers from electrical hazards.
- Ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations.
- Reduce the risk of electrical injuries, fatalities, and equipment damage.
-
Importance of Electrical Safety
- Prevents injuries, fatalities, and equipment damage.
- Ensures safe working environments.
- Promotes compliance with NFPA 70E and other safety regulations.
-
Overview of NFPA 70E
- Provides guidelines for electrical safety in the workplace.
- Includes requirements for safe work practices, training, and PPE.
- Aims to protect workers from electrical hazards like shock, arc flash, and arc blast.
-
Applicability of NFPA 70E on Oil and Gas Rig Sites
- Applies to all workers involved in electrical work on rigs.
- Ensures safe handling and maintenance of electrical equipment.
- Addresses specific risks associated with the oil and gas industry.
-
Who Should Follow This Standard?
- All employees working on or near electrical installations.
- Employers and supervisors responsible for electrical safety.
- Electrical contractors and maintenance personnel.
-
Environments Covered by NFPA 70E
- Industrial and commercial facilities.
- Construction sites and maintenance areas.
- Any workplace with electrical systems and equipment.
-
Arc Flash
- A dangerous release of energy caused by an electrical arc.
- Can result in severe burns, injuries, and fatalities.
- Requires specific safety measures and PPE to mitigate risks.
-
Arc Rating
- A measure of the protective performance of PPE against arc flash.
- Indicates the amount of energy the clothing can withstand before the wearer receives a second-degree burn.
- Essential for selecting appropriate PPE.
-
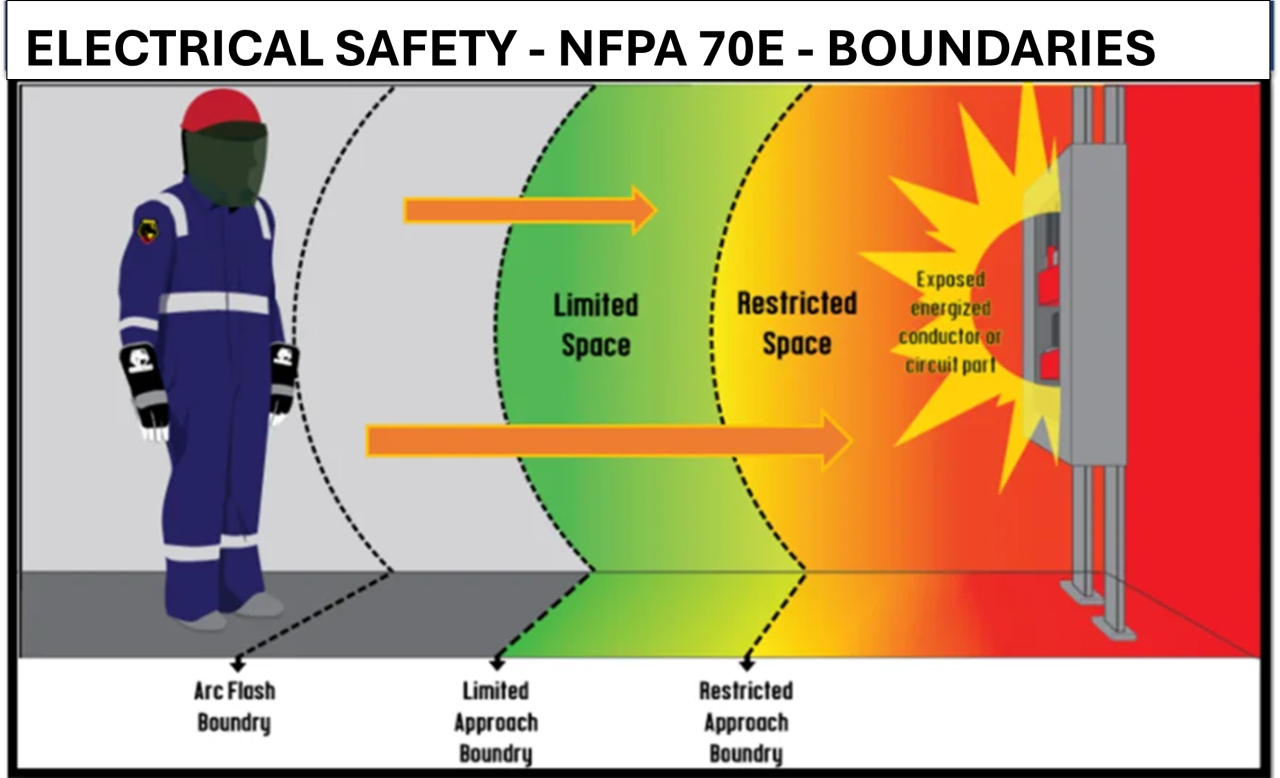
Boundaries as per NFPA 70E
- Limited Approach Boundary: Distance within which a shock hazard exists.
- Restricted Approach Boundary: Closer distance where only qualified personnel can work.
- Prohibited Approach Boundary: Area very close to live parts; no work is allowed without de-energizing.
-
Electrically Safe Work Condition
- A state where electrical equipment is de-energized and locked out to prevent accidental energization.
- Includes verifying the absence of voltage and grounding equipment.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Essential for protecting workers from electrical hazards.
- Includes arc-rated clothing, insulated gloves, face shields, and other equipment.
- Must be selected based on the specific hazards present.
-
Qualified Person
- An individual with the training and knowledge to recognize and avoid electrical hazards.
- Must be able to perform tasks safely according to NFPA 70E standards.
-
Unqualified Person
- A person who has not been trained or authorized to work on or near exposed electrical conductors or equipment.
- Should be kept at a safe distance from electrical hazards.
-
Electrical Hazard Risk Assessment
- A systematic process to identify, assess, and mitigate electrical hazards.
- Involves evaluating the potential for electrical shock, arc flash, and other risks.
- Helps in determining appropriate safety measures and PPE.
-
Job Safety Planning and Job Briefings
- Essential for ensuring safety before starting any electrical work.
- Includes hazard identification, risk assessment, and defining safety procedures.
- Involves conducting pre-job briefings to communicate safety information to all workers.
-
Establishing an Electrically Safe Work Condition
- De-energize equipment and isolate it from all energy sources.
- Lockout/tagout procedures must be followed.
- Verify the absence of voltage and apply grounding if necessary.
-
Electrical Safety Program
- A comprehensive program to manage electrical safety in the workplace.
- Includes training, hazard assessments, maintenance procedures, and emergency response plans.
- Aims to reduce the risk of electrical accidents and ensure compliance with NFPA 70E.
-
Work Involving Electrical Hazards
- Specific tasks that require heightened safety measures and potentially an energized electrical work permit.
- Includes tasks like testing, troubleshooting, and certain maintenance activities.
-
Tasks that Require an Energized Electrical Work Permit
- Tasks where de-energizing equipment is not feasible.
- Must include a detailed job safety plan and risk assessment.
- Requires authorization and additional safety measures.
-
Risk Assessment Procedures
- Identify hazards, assess the level of risk, and implement control measures.
- Continuously review and update assessments as needed.
- Involve both engineering and administrative controls to mitigate risks.
-
Purpose of Arc Flash Hazard Analysis
- Determine the potential incident energy of an arc flash.
- Establish safe working distances and appropriate PPE requirements.
- Ensure worker safety and compliance with NFPA 70E.
-
Determining Arc Flash Boundaries
- Calculate the distance from an electrical source within which a person could receive a second-degree burn.
- Use this information to establish safety zones and PPE requirements.
-
Incident Energy Analysis
- A detailed analysis to quantify the energy released during an arc flash.
- Helps in determining the appropriate level of PPE and safety measures.
-
Importance of Maintenance
- Regular maintenance ensures electrical systems operate safely and efficiently.
- Prevents equipment failures and reduces the risk of electrical hazards.
- Includes routine inspections, testing, and repairs.
-
Maintenance Procedures
- Clearly defined steps for performing maintenance on electrical systems.
- Must include safety measures such as LOTO and PPE use.
- Ensure that only qualified personnel perform maintenance tasks.
-
Documentation of Maintenance
- Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities.
- Include dates, tasks performed, and any issues identified and addressed.
- Helps in tracking equipment performance and identifying recurring problems.
-
Procedures for Electrical Accidents
- Have clear protocols for responding to electrical accidents.
- Include first aid measures, emergency contacts, and reporting procedures.
- Ensure all employees are trained on these procedures.
-
First Aid for Electrical Shock
- Do not touch the victim directly if they are still in contact with the electrical source.
- Disconnect the power source and call emergency services.
- Provide CPR if necessary and treat burns or other injuries appropriately.
-
Fire Response
- Do not use water to extinguish electrical fires.
- Use Class C fire extinguishers (dry chemical or CO2).
- Evacuate the area if the fire cannot be controlled and call emergency services.
-
Real-life Examples of Electrical Accidents
- Learn from real incidents to understand the importance of electrical safety.
- Examples include arc flash incidents, electrocutions, and electrical fires.
- Highlight the need for strict adherence to safety protocols and preventive measures.
-
Lessons Learned
- Always wear appropriate PPE and follow safety procedures.
- Implement and enforce LOTO programs.
- Conduct thorough hazard assessments and regular inspections.
- Provide continuous training and promote a culture of safety.
-
Preventive Measures
- Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical systems.
- Proper use of PPE and adherence to LOTO procedures.
- Comprehensive safety training and clear safety protocols.
- Effective emergency preparedness and response plans.
Nutshell
By following these key points and implementing comprehensive preventive measures, organizations can enhance electrical safety, protect their employees, and ensure compliance with NFPA 70E standards