Introduction
In high-risk industries such as construction, oil & gas, manufacturing, and electrical maintenance, a robust Permit to Work (PTW) system is essential for ensuring safety and compliance. PTW systems—also referred to as work authorization permits—are formal, written systems used to control certain types of work that are identified as potentially hazardous.
Organizations like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE) mandate that hazardous activities be authorized, planned, and executed under controlled conditions. A well-designed PTW system minimizes the likelihood of accidents by ensuring that tasks are only carried out under safe conditions and with full awareness of associated risks.
What is a Permit to Work System?
A Permit to Work system, as defined by OSHA, is a “documented procedure that authorizes certain people to carry out specific work within a defined time frame under controlled conditions” (OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart J).
It specifies:
- What work will be done
- Who will perform it
- Where and when it will be carried out
- The safety measures required
This system also acts as a communication tool between those who authorize the work and those who carry it out, while documenting that all hazards have been assessed and controlled.
Why Is a PTW System Necessary?
According to HSE Guidance HSG250, a PTW is not just a paper exercise—it is a key part of safe systems of work, particularly for non-routine tasks or those involving significant hazards.
Situations that typically require a PTW include:
- Hot Work: Welding, cutting, brazing, or using open flames
- Confined Space Entry: Tanks, vessels, silos, sewers
- Electrical Work: Maintenance, installation, or decommissioning
- Work at Height: Roof maintenance, scaffolding
- Excavation or Demolition: Potential for collapse, underground services
The goal is not only to prevent accidents but also to ensure regulatory compliance with standards like OSHA, ISO 45001:2018, and national labor safety codes.
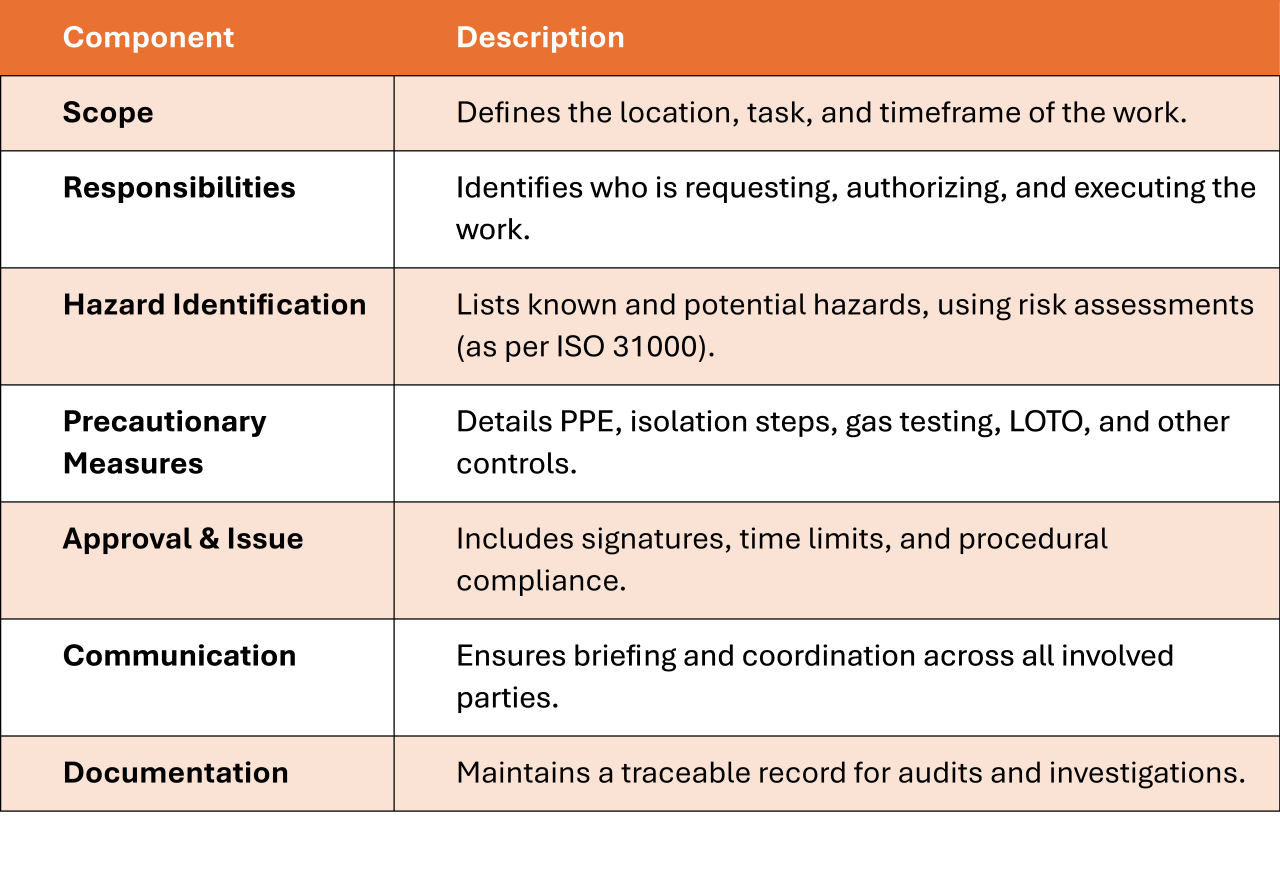
Core Components of a PTW System
A compliant PTW system typically includes:
Common Types of Work Permits
Different activities require tailored permits to ensure hazards are addressed adequately:
-
Hot Work Permit
For tasks involving flame, spark, or heat (e.g., welding, cutting). Refer to [NFPA 51B – Fire Prevention for Hot Work].
-
Cold Work Permit
For tasks involving chemical hazards or tools that don’t generate ignition but pose other risks (e.g., maintenance, scaffolding erection).
-
Confined Space Entry Permit
Required for enclosed or partially enclosed spaces. Must comply with [OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146] and include atmospheric testing and rescue plans.
-
Electrical Work Permit
For tasks involving energized systems. Must follow [NFPA 70E] and define arc flash and shock hazards.
-
General Work Permit
For hazardous tasks not classified under other permit types.
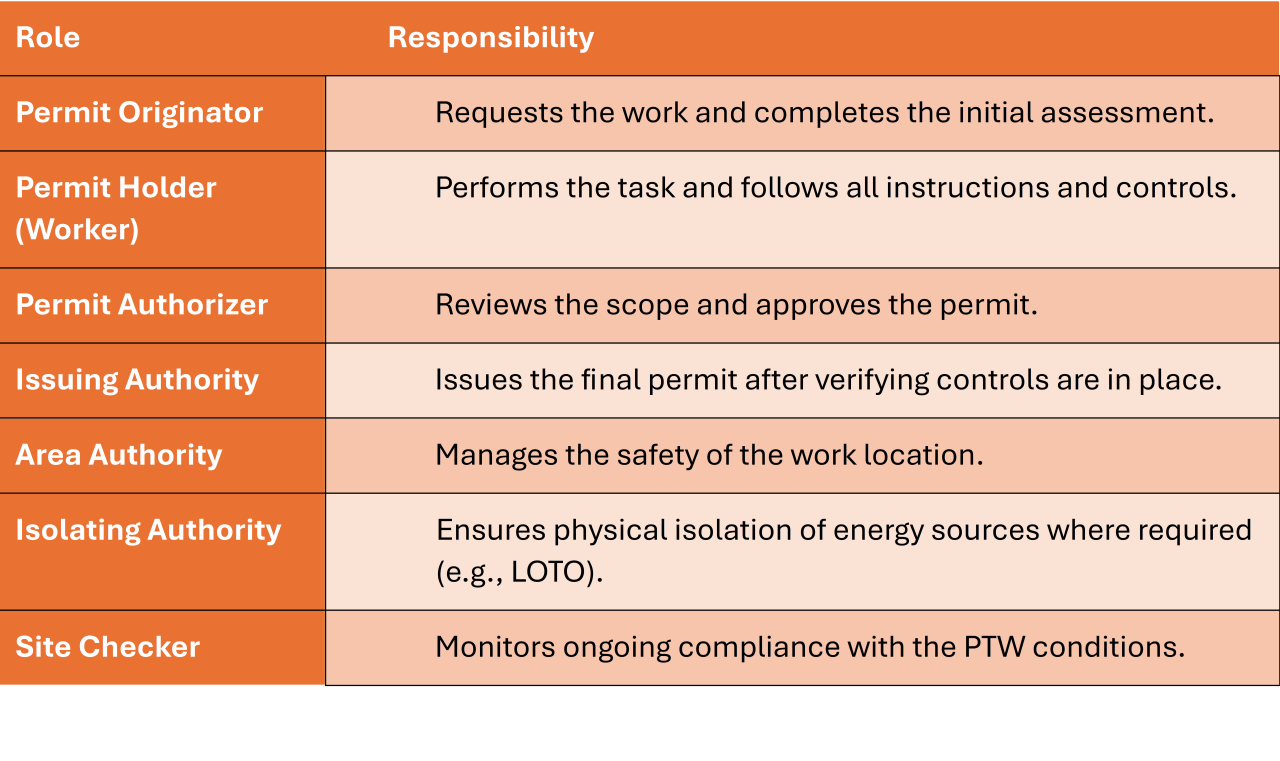
Roles and Responsibilities
Key Compliance Elements (OSHA and HSE Aligned)
- Hazard Evaluation: Identify the task-specific risks.
- Training: Workers must be trained in PTW use, hazard awareness, and PPE.
- Monitoring: Regular inspections to verify adherence.
- Communication: Clear handover procedures and briefings.
- Isolation Procedures: Energy isolation using LOTO (Lockout-Tagout) protocols.
Benefits of an Effective PTW System
✔️ Prevents unauthorized and unsafe work
✔️ Promotes hazard awareness
✔️ Encourages cross-functional communication
✔️ Supports legal and regulatory compliance
✔️ Provides a documented safety trail for audits and incident investigations
Digitizing the PTW System
Modern EHS (Environment, Health & Safety) software solutions streamline the PTW process by:
- Centralizing permits and documentation
- Providing real-time updates and notifications
- Enhancing traceability and compliance tracking
- Supporting mobile access for remote or field teams
ISO 45001:2018 also encourages the use of digital systems to improve occupational health and safety performance.
References
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910 – osha.gov
- HSE Guidance HSG250 – Guidance on Permit to Work Systems
- NFPA 51B – Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding
- NFPA 70E – Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
- ISO 45001:2018 – Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
- ISO 31000 – Risk Management – Principles and Guidelines